HYDROGEN BREATH TEST
⦁ HBT is a simple, non-invasive test based on analysis of breath hydrogen using breath test analyzer.
⦁ It is used for diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders like lactose/fructose/IBS/ other sugar intolerance, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), intestinal malabsorption , gastrointestinal dysmotility, etc.
C-13 UREA BREATH TEST FOR H.Pylori
⦁ UBT is a simple, non-invasive test based on analysis of breath carbon- dioxide (C-13 labeled) using breath test analyzer.
⦁ Unlike the urea breath test carried out using radioactive C-14 isotope of carbon, it is quite safe being a non radioactive isotope and can be used for diagnosis even in pregnant ladies and kids.
⦁ It is used for the diagnosis of a bacterium, Helicobacter pylori (H.Pylori) in the stomach, that leads to symptoms of gastritis, and if left untreated causes gastric ulcers or in some individuals, gastric carcinoma.
24 Hr. ESOPHAGEAL PH MONITORING
⦁ This is a test used to evaluate the Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and to determine the efficacy and adequacy of the surgery and anti-reflux medicines. It measures the degree of acidity / alkalinity (i.e. pH) , duration and frequency of gastric content refluxing from stomach to the esophagus.
⦁ To evaluate whether the patient has gastroesophageal reflux disease or whether antacid medications are adequate to suppress acid production (in the presence of typical symptoms of GERD like, heartburn and regurgitation).
⦁ To determine whether, atypical symptoms of GERD such as chest pain, coughing, wheezing, hoarseness, sore throat, burping, asthma and dental erosion are due to gastroesophageal reflux.
⦁ Part of pre- operative evaluation of anti reflux surgery.
24 Hr. ESOPHAGEAL IMPEDANCE- PH MONITORING
⦁ This is a test used to evaluate the Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and to determine the efficacy and adequacy of the surgery and anti-reflux medicines. It measures the degree of acidity / alkalinity (i.e. pH) , type , extent, duration and frequency of gastric content refluxing from stomach to the esophagus.
⦁ To evaluate whether the patient has gastroesophageal reflux disease or whether antacid medications are adequate to suppress acid production (in the presence of typical symptoms of GERD like, heartburn and regurgitation).
⦁ To determine whether, atypical symptoms of GERD such as chest pain, coughing, wheezing, hoarseness, sore throat, burping, asthma and dental erosion are due to gastroesophageal reflux.
⦁ It gives an idea of symptom association probability of reflux with any typical/ atypical symptoms
⦁ In addition, it helps to differentiate patients with functional heartburn.
STATIC GASTRIC PH MONITORING
⦁ This is a test used to evaluate the intensity of Gastric acidity.
⦁ As an additional tool to endoscopy for diagnosing atrophic gastritis.
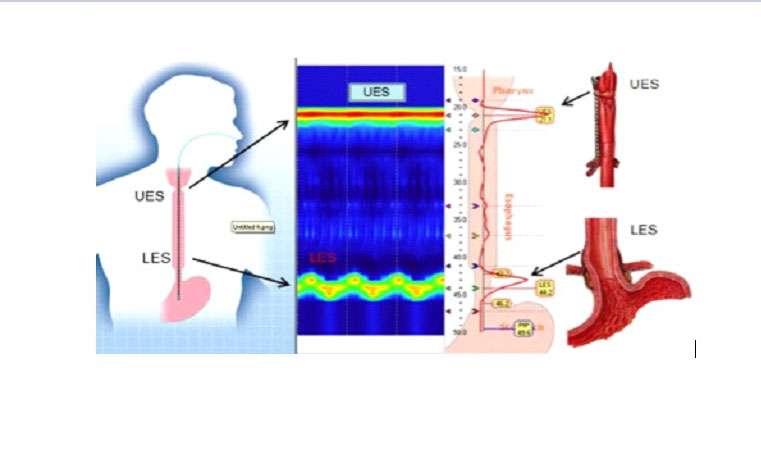
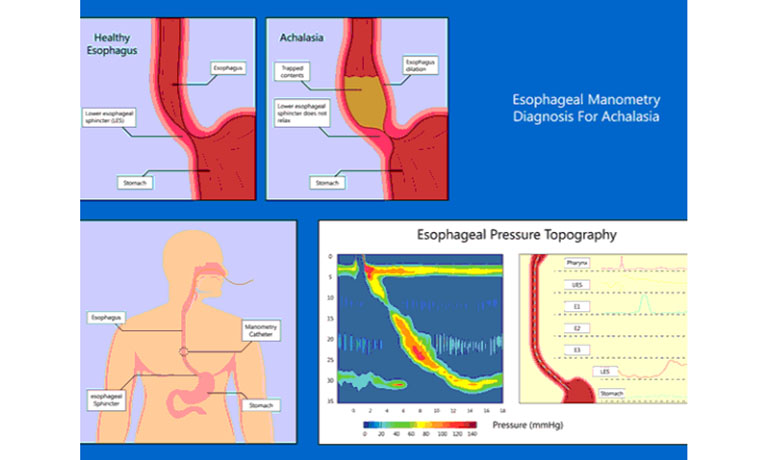
HHIGH RESOLUTION ESOPHAGEAL MANOMETRY
⦁ This is a procedure that measures the strength and function of the muscles and valves in your esophagus (the “food pipe”) that work to push food and liquids from the mouth down to the stomach.
⦁ To evaluate the cause of reflux of stomach acid and contents back into the esophagus (gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD).
⦁ To determine the cause of problems with swallowing food, such as food or liquids getting stuck in the chest after swallowing.
⦁ To evaluate patients with chest pain that may be coming from the esophagus rather than the heart.
HIGH RESOLUTION ANORECTAL MANOMETRY
⦁ This is a test performed to evaluate patients with constipation or fecal incontinence. This test measures the pressures of the anal sphincter muscles, the sensation in the rectum, and the neural reflexes that are needed for normal bowel movements.
⦁ Fecal incontinence (can’t control bowels, resulting in fecal leakage).
⦁ Constipation (less than three bowel movements a week).
⦁ Hirschsprung’s disease in children (a disease that can cause a blockage in the large intestine).
BIOFEEDBACK THERAPY FOR CONSTIPATION & FECAL INCONTINENCE
⦁ An instrument-based learning process centered on operant conditioning. In a broader sense, includes education, counseling, and diaphragmatic muscle training as well as exercise, sensory, and coordination training.
⦁ The goal of biofeedback therapy in defecatory disorders is to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, retrain rectal sensation and coordinate pelvic floor muscles during evacuation.
COLON TRANSIT STUDY (USING RADIOOPAQUE MARKERS)
⦁ The most basic and primary tool in evaluating disorders of colonic motility. Helpful in pathologic diagnosis and for planning management in patients with constipation
⦁ Radioopaque marker testing distinguishes constipation subgroup such as normal or slow transit constipation, and assesses segmental transit times in patients with delayed total colon transit.
⦁ Simple and inexpensive as well as reliable and reproducible
ELECTROGASTROGRAPHY
⦁ Electrogastrography (EGG) is a recording of the myoelectric signals from the stomach as an aid to diagnosis of various gastric motility disorders.
⦁ It is quite safe being a totally noninvasive procedure that doesn’t disturb ongoing physiologic activities and can be used for diagnosis even in geriatric and pediatric populations.
⦁ It is used as an adjunct to esophagogastroduodenoscopy (Endoscopy or EGD) for the diagnosis of various disorders related to gastric dysrhythmias like GERD, functional dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting, post prandial fullness, early satiety, gastroparesis and functional pyloric outlet obstruction.
Quick Point of care tests for Rapid diagnosis:
CELIAC RAPID TEST: for the qualitative detection of antibodies (IgA/IgG/IgM) against human tissue transglutaminase in a drop of blood to rule out wheat (gluten) allergy.
FECAL CALPROTECTIN TEST: a diagnostic tool to distinguish between inflammatory bowel disease and functional bowel disorders and to assess the disease activity, drug dosage modifications and to predict recurrence.
GASTROPANEL ELISA TEST: to diagnose symptomatic dyspepsia and screening the risks of gastric carcinoma.
LACTOSE INTOLERANCE QUICK (BIOPSY) TEST: sensitive test to detect lactase deficiency and to predict the clinical response to a lactose- free diet accurately.
PEPTEST: to identify GERD, EOR, LPR, chronic cough, cystic fibrosis, lung allograft rejection, otitis media with effusion, asthma, sinusitis, voice problem, hoarseness, frequent throat clearing, heartburn.
CELIAC RAPID TEST: for the qualitative detection of antibodies (IgA/IgG/IgM) against human tissue transglutaminase in a drop of blood to rule out wheat (gluten) allergy.
This is a procedure that measures the strength and function of the muscles and valves in your esophagus (the “food pipe”) by analyzing pressures and the pattern of muscle contractions in a way that aids in the evaluation of esophageal motility disorders.
Indications
⦁ Heartburn and/or regurgitation of food (gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD).
⦁ Establish the etiology of disorders like achalasia and esophageal spasm with the presenting symptoms, such as
difficulty swallowing (Dysphagia),
pain felt during swallowing (Odynophagia).
⦁ Evaluate patients with chest pain that may be coming from the esophagus rather than the heart (e.g. Jackhammer’s esophagus).
⦁ Pre- operative assessment (conditions that resemble GERD and cannot be helped by GERD surgery) for anti-reflux surgery or anti- reflux procedure to treat GERD.
Pre- procedure
⦁ Do not eat or drink anything 5-6 hours before the procedure.
⦁ Bring along the previous investigation reports such as any blood tests, Barium swallow , CT scan or MRI.
During procedure
⦁ No sedation is given for the procedure.
⦁ A topical anesthetic lubricated high resolution manometry catheter having a small diameter is passed through the nares into the nasopharynx and navigated down the esophagus into the stomach, in an upright position.
⦁ The catheter connected to the device, does not interfere with the breathing and is placed in about a minute and fixed.
⦁ Then the patient is asked to lie on his/her left side.
⦁ After this the patient is given a 5cc bolus of water ten times to swallow.
⦁ The catheter having the pressure sensors, evaluates the strength and coordination of muscle contractions and also assesses the strength and relaxation function of the lower esophageal sphincter/valve.
⦁ At the end of last swallow, the catheter is slowly and carefully taken out.
Post procedure
⦁ Performed as an outpatient procedure, lasting 20-30 minutes.
⦁ Normal diet and activities may be resumed immediately after the test.
⦁ A temporary sore throat may be felt, that can be taken care of with saline gargles.




